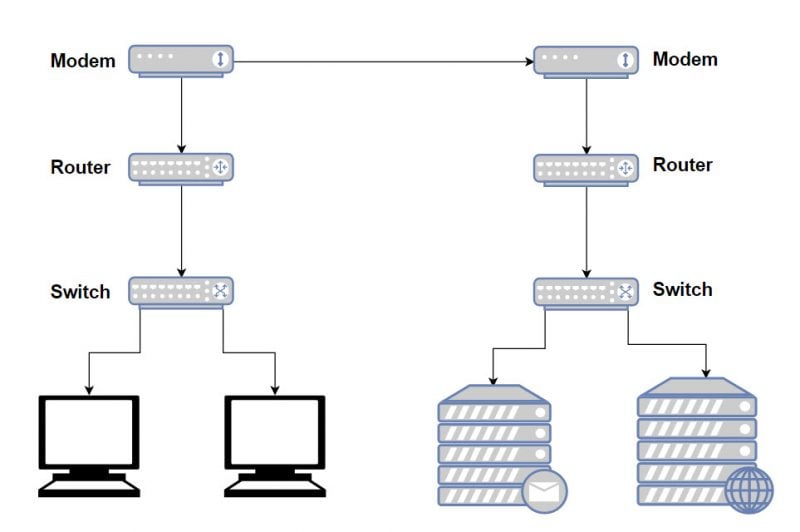
In the computer networking world, the three most ubiquitous pieces of equipment are modems, routers, and switches. These are used everywhere from the datacenter hosting Google to the internet connection in your own home. However, despite how important these three pieces of equipment are, many people are completely oblivious as to what each piece of equipment does, so in this article, we’ll attempt to clarify the difference between the modem, router and switch, and how it all fits in your home network.
OSI Reference Model
Before we start with the modem vs router vs switch conversation, we first need to understand the OSI Reference Model, or Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model. The OSI Reference Model is a framework originally developed in 1984 by the ISO (International Organization of Standardization) that essentially governs how information is communicated through a network. As modems, routers and switches are network devices, they fall under the OSI Reference Model. This is why a router made by Cisco will work with a switch made by Netgear, and the switch made by Netgear will work with a Wi-Fi access point made by TP-Link.
In total there are 7 layers in the OSI Reference Model. Below is an overview of what each layer is called and what type of data is carried in the layer.
| Layer | Layer Name | Protocol Data Unit | Common Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physical | Bit | 10/100/1000 Ethernet, 802.11a/b/g/n/ac |
| 2 | Data-link | Frame | MAC, Frame Relay |
| 3 | Network | Packet | IP, OSPF, RIP |
| 4 | Transport | Segment / Datagram | TCP, UDP |
| 5 | Session | Data | RPC, SQL |
| 6 | Presentation | Data | SSL, TLS |
| 7 | Application | Data | HTTP, FTP |
If the chart above seems a little confusing, this is understandable, so let’s dive a little more in depth into each device and discuss how it relates to each layer of the OSI Reference Model.
What is a Modem?
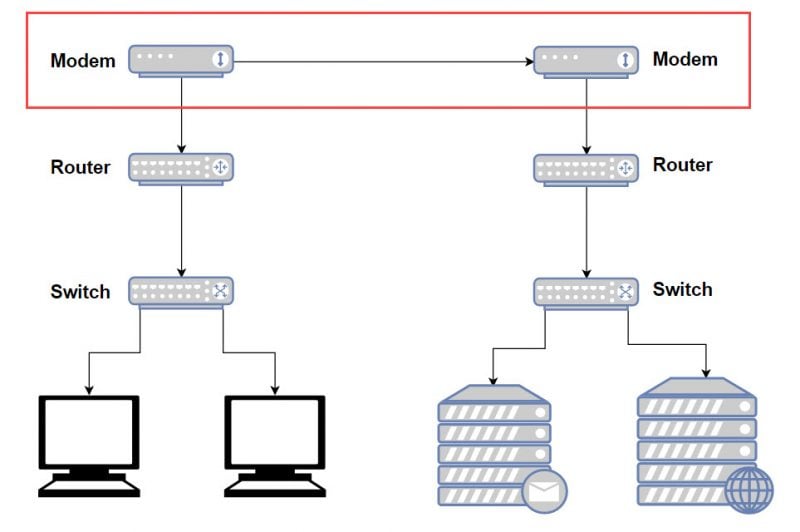
A modem is the short way of saying “modulator, demodulator”. The primary purpose of a modem when used in a home networking environment is to establish a connection between your home internet connection and your ISP.
Now you may ask, why is this necessary? Well, the reason why we need modems is because unlike a router or a switch, different types of modems can transmit and receive data on different types of physical connections. For example, a DSL modem is capable of transferring data over a standard copper telephone line, a cable modem is capable of transferring data over a coax cable line, a fiber modem is capable of transferring data over a fiber optic line, a satellite modem is capable of transferring data over a satellite connection, and well, you get the gist. Each type of modem is capable of transferring data over a different type of physical connection using a set of communications standards, or protocols, that it was designed to support.
In the OSI Reference Model, the modem is considered a Layer 1 device. Modems transmit bits, which are essentially 0s and 1s. This is the most basic form of data.
What is a Router?
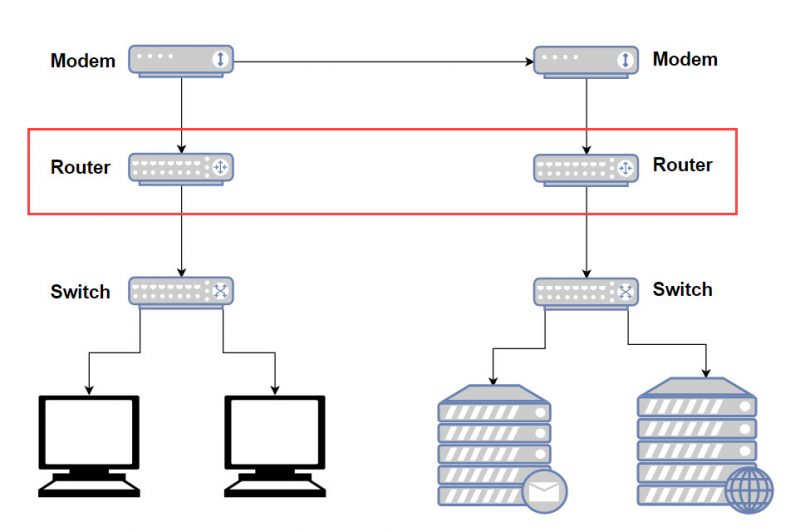
A typical home router is designed to route data between different networks using IP, or Internet Protocol. Whereas a modem simply establishes a connection between your home network and your ISP, a router helps facilitate communications between your home’s network and the ISP’s network. This is why your computer’s IP address on your home network is different than the public IP address your ISP assigned you.
In the OSI Reference Model, the router is considered a Layer 3 device. Routers transmit packets and more importantly have the capability to transmitting data through different networks.
Typically, home routers also include built-in switches in order to provide the ability for multiple devices to be connected on the same network. Business or enterprise routers on the other hand may not include this functionality and requires a separate, standalone switch for this purpose.
What is a Switch?
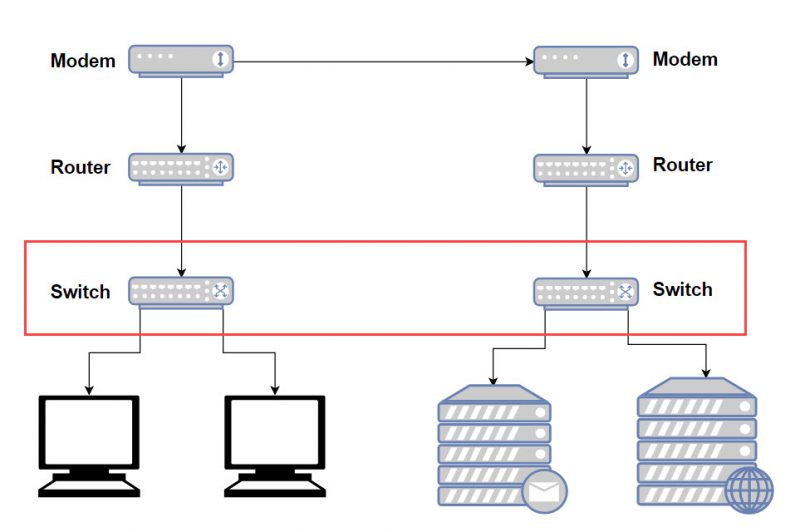
A switch is simply a device that connects multiple devices on the same network. Unlike a router which is capable of creating and routing between multiple TCP/IP networks, a switch is a device that’s designed only to facilitate communications for devices on the same network.
In the OSI Reference Model, the switch is considered a Layer 2 device. Switches generally help forward frames inside a network. However, recent introductions of newer enterprise switches have blurred the lines in terms of where the devices fall under in the OSI Reference Model. The reason for this is because many of the newer switches are called switches however, they have capability across Layers 2 to 7 including functionality such as routing, web switching, cookie switching, and more.
Modem/Router Combo Devices
While many modems are simply just modems, there are many modems that are also modem/router combos which are not only capable of performing the duties of the modem, but are also capable of routing and switching as well.
In the case of the combo modem and router, the device actually contains a modem, router, switch, and wireless access point bundled into one. This is typically found in home networks as it makes it easy on the ISP since only a single device needs to be provided to a customer for them to access the internet.

Thanks Sam, my job is transitioning from a Field Service Tech building and servicing electro-mechanical-plc equipment to aiding in the installation of SCADA associated equipment. I only hope this 70+ year old brain will be flexible enough to understand the process.